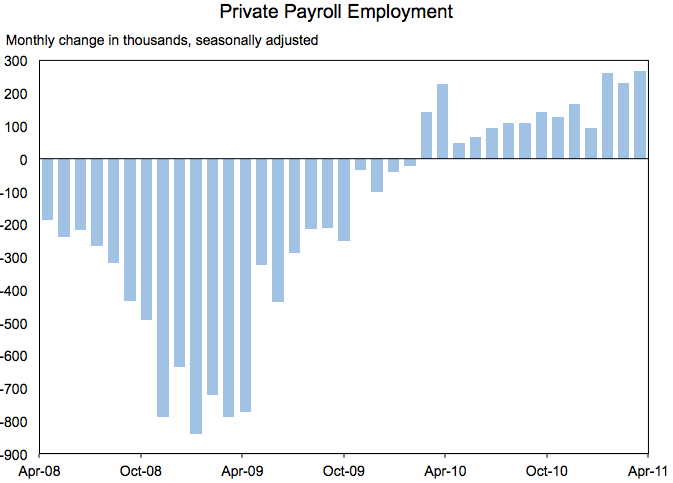
Today’s employment report shows that private sector payrolls increased by 268,000 in April, the strongest monthly growth in five years. The economy has added 2.1 million private sector jobs over 14 consecutive months, including more than 800,000 jobs since the beginning of the year. The unemployment rate rose to 9.0 percent, but remains 0.8 percentage point below its November level.
Despite headwinds from high energy prices and disruptions from the disaster in Japan, the last three months of private job gains have been the strongest in five years.While the solid pace of employment growth in recent months is encouraging, faster growth is needed to replace the jobs lost in the downturn. We are seeing signs that the initiatives put in place by this Administration – such as the payroll tax cut and business incentives for investment – are creating the conditions for companies to add new jobs and foster the industries of the future. We will continue to work with Congress to find ways to reduce spending, so that we can live within our means without neglecting the investments in education, infrastructure, and clean energy that will strengthen our economy.
In addition to the increases last month, payroll survey estimates of private sector job growth for February (now +261,000) and March (now +231,000) were revised up. Overall payroll employment rose by 244,000 in April, well above market expectations. Payroll employment grew in almost every sector. Solid employment increases occurred in retail trade (+57,100), professional and business services (+51,000), education and health services (+49,000), leisure and hospitality (+46,000), and manufacturing (+29,000). Manufacturing has added 244,000 jobs in the last 14 months, the best period of manufacturing job growth in 13 years. State and local government experienced a decline of 22,000; this sector has shed 289,000 jobs in the past 14 months, mostly in local government.
The unemployment reading in April showed a partial reversal of the 1.0 percentage point decline over the previous four months. Employment measured in the household survey dipped in April and the labor force participation rate was unchanged. The unemployment rate data derive from a separate household survey. The payroll and household surveys can differ on a monthly basis; the household survey is more volatile, but the two surveys typically show similar long-run trends in employment.
The overall trajectory of the economy has improved dramatically over the past two years, but there will surely be bumps in the road ahead. The monthly employment and unemployment numbers are volatile and employment estimates are subject to substantial revision. Therefore, as the Administration always stresses, it is important not to read too much into any one monthly report.
Austan Goolsbee is Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers