The economy added jobs in September at a pace below that seen earlier in the year, as slowing growth abroad and global financial turmoil have weighed on economic activity. Overall, however, the unemployment rate remains at its lowest level since early 2008 and the private sector has added 13.2 million jobs over 67 straight months of job growth—the longest streak on record. Given the increased uncertainty around the world, it is imperative that the United States not further exacerbate that uncertainty with unnecessary brinksmanship and austerity. Instead, we must take steps to continue the domestic momentum that the U.S. economy has enjoyed in the last several years. That includes passing a budget that reverses the sequester and makes critical investments that help our economy continue to grow, reauthorizing the Ex-Im Bank so that our businesses can compete on a level-playing field abroad, and increasing investments in infrastructure.
FIVE KEY POINTS ON THE LABOR MARKET IN SEPTEMBER 2015
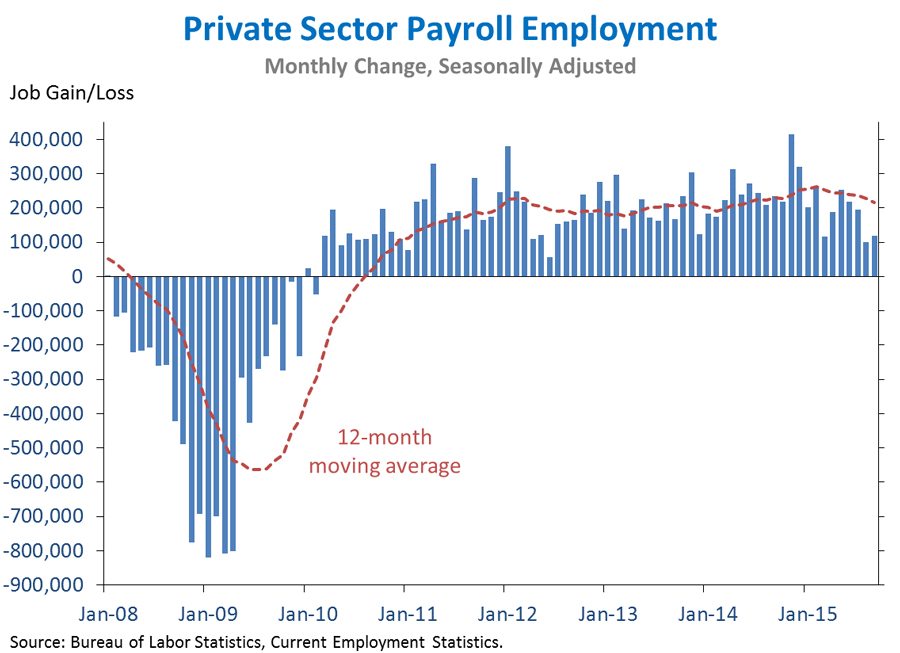
1. Today we learned that private-sector employment rose by 118,000 in September, below the pace observed earlier in the year. However, September was the 67th straight month of private sector job growth, extending the longest streak on record. The unemployment rate held steady at 5.1 percent, its lowest level since early 2008, while the labor force participation rate decreased. Wages were largely unchanged over the month, with nominal average hourly earnings for all private-sector workers up 2.2 percent over the past year. Payroll employment growth in July and August were revised downward.
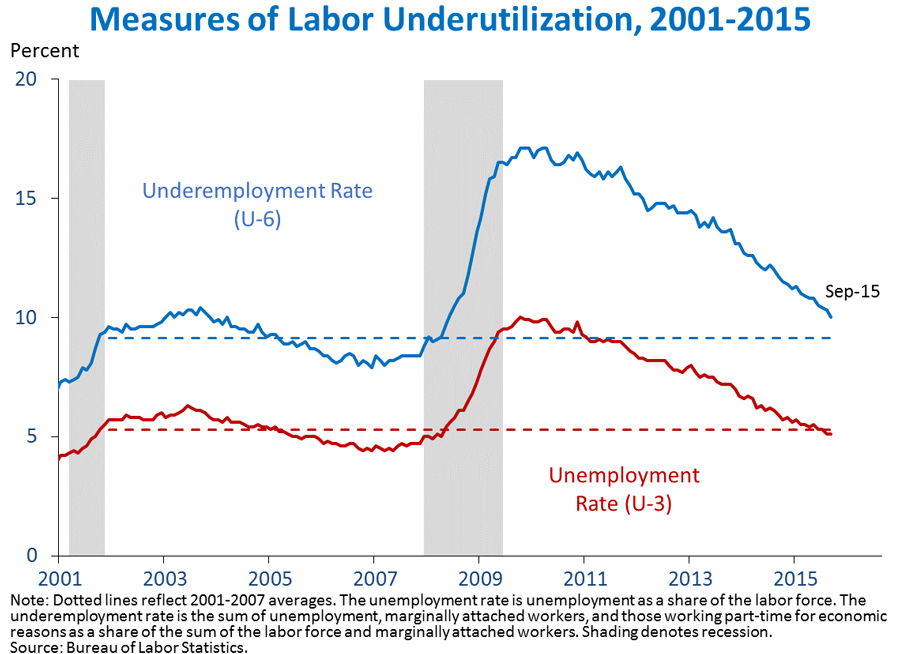
2. The underemployment rate declined 0.3 percentage point to 10.0 percent in September, its lowest level since May 2008. While the headline unemployment rate (U-3) measures only unemployed persons, the underemployment rate (U-6) also includes those who are “marginally attached” to the labor force but not actively looking for a job, and those employed part-time who would prefer to work full-time. Although the headline unemployment rate was unchanged in September, the underemployment rate fell 0.3 percentage point as the share of the labor force working part-time for economic reasons fell from 4.1 percent to 3.9 percent. Over the last year, the underemployment rate declined 1.7 percentage points, compared with a 0.8 percentage point decline for the official unemployment rate. Despite this recent progress, part-time employment for economic reasons remains elevated, and the underemployment rate has not fully returned to its pre-crisis average.
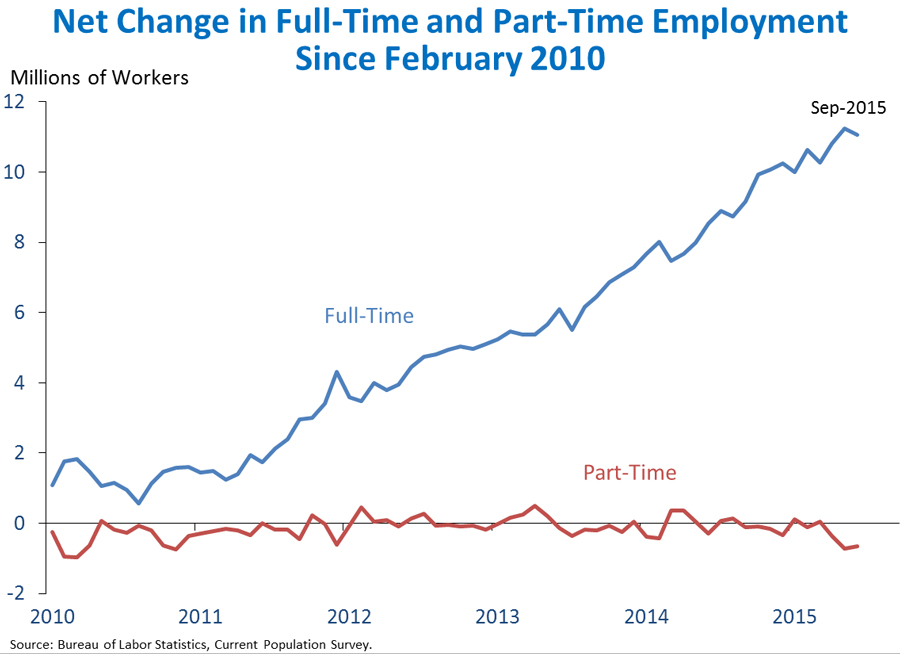
3. The rise in employment since early 2010 is more than fully accounted for by the increase in full-time employment, with part-time employment holding steady. The economy has added 11 million full-time jobs since February 2010, according to a separate survey of households that measures full-time and part-time status. Part-time employment has fallen slightly over this period. While 75 percent of part-time workers do so for family, health, and other reasons, the fraction of the labor force working part-time for economic reasons declined in September. This shift drove the reduction in the underemployment rate to its lowest level since May 2008.
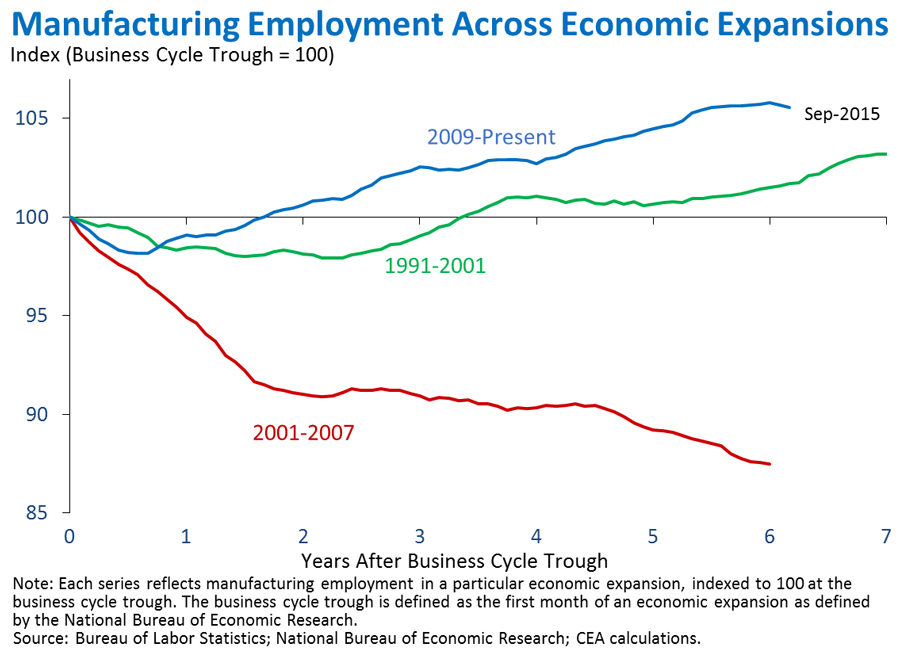
4. Manufacturing job growth has been stronger in this recovery than in previous expansions. American manufacturers have created 865,000 jobs since February 2010, including net gains in 2015 despite decreases during the last two months. In fact, manufacturing employment declined over the decade leading up to the financial crisis, even during the 2001-2007 economic expansion. Manufacturing employment fell 12.5 percent over that period, despite the 18.0 percent increase in gross domestic product. The trend has reversed in this recovery, with manufacturing employment currently 5.6 percent above its level when the recession ended in 2009. The 1991-2001 expansion did see manufacturing employment growth, but at a considerably slower pace—at the corresponding point in that expansion, manufacturing employment was only 1.7 percent higher than the business cycle trough. Notwithstanding the outsized progress in this expansion compared with previous expansions, manufacturing has not yet fully recovered the losses in incurred during the Great Recession.
5. The distribution of job growth across industries in September generally followed recent trends, with this month’s slower growth affecting a number of industries. Despite the overall pace of job growth, above-average gains relative to the past year were seen in information services (+12,000) and State and local government (+26,000). September was an especially weak month in wholesale trade (-4,000), utilities (-1,000), and financial activities (unchanged). Across the 17 industries shown below, the correlation between the most recent one-month percent change and the average percent change over the last twelve months remained essentially unchanged at 0.94.
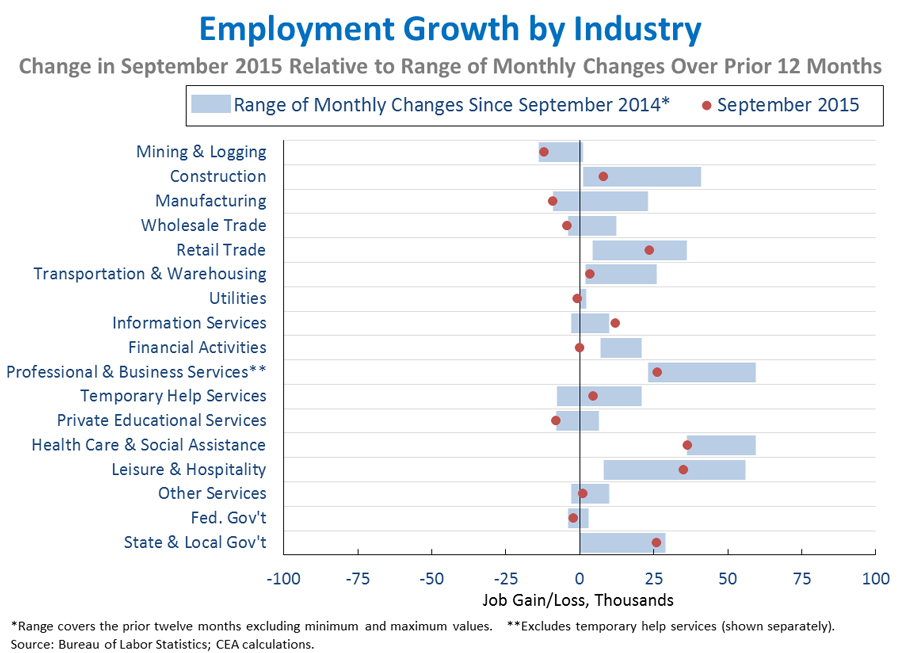
As the Administration stresses every month, the monthly employment and unemployment figures can be volatile, and payroll employment estimates can be subject to substantial revision. Therefore, it is important not to read too much into any one monthly report, and it is informative to consider each report in the context of other data as they become available.
Jason Furman is Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers.


